Binary tree is a non-linear data structure.Basically a hierarchical data structure composed of nodes, where each node has at most two children, referred to as the left child and the right child. The top node of the tree is called the root.
So in Binary tree we can add our data in a fome of nodes and for traversing searching that particular element. We have different type of algorithms . DFS is one of them
DFS stands for depth first search
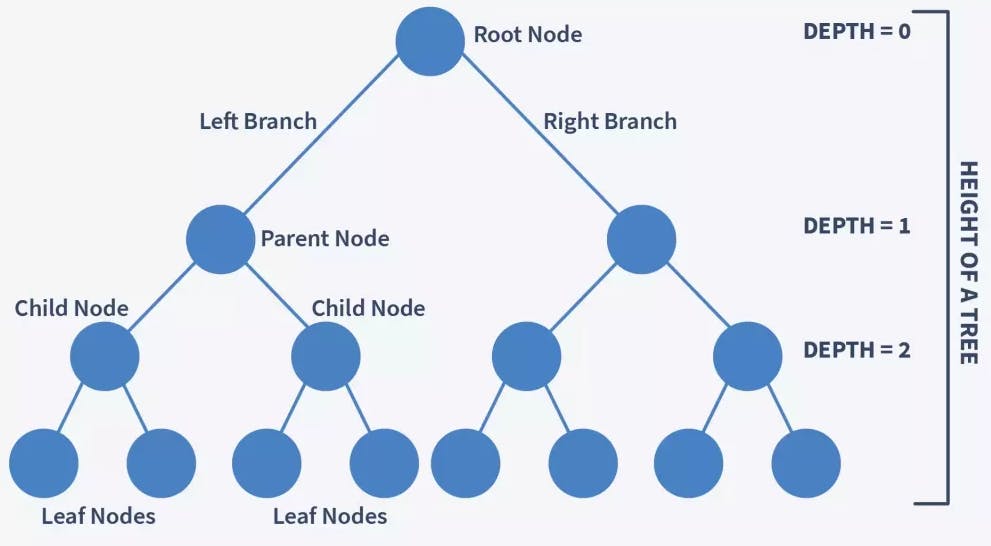
DFS involves visiting nodes in depth-first order, meaning it explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
There are three common methods to perform DFS on a binary tree:
Inorder Traversal: In an inorder traversal, the nodes are visited in the order of left subtree, current node, and then right subtree.
Inorder:- Left →Parent →Right
Preorder Traversal: In a preorder traversal, the current node is visited first, followed by the left subtree and then the right subtree.
Preorder:- Parent →Left →Right
Postorder Traversal: In a postorder traversal, the left subtree is visited first, then the right subtree, and finally the current node.
Postorder:- Left →Right →Parent
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Node structure for binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
// initialize
Node(int value){
val = value;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
// inorder Traversal
void inorderTraversal(Node* node){
// base case
if(node == nullptr){
return;
}
inorderTraversal(node->left);
std::cout << node->val <<" "<< std::endl;
inorderTraversal(node->right);
}
// PreOrderTraversal
void PreOrderTraversal(Node* node){
// base case
if(node == nullptr){
return;
}
std::cout << node->val << std::endl;
PreOrderTraversal(node->left);
PreOrderTraversal(node->right);
}
// PostOrderTraversal
void PostOrderTraversal(Node* node){
// base case
if(node == nullptr){
return;
}
PostOrderTraversal(node->left);
PostOrderTraversal(node->right);
std::cout << node->val<< std::endl;
}
int main(){
// creating a Binay tree
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
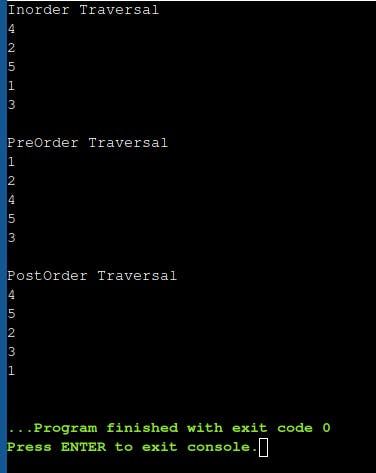
std::cout << "Inorder Traversal" << std::endl;
inorderTraversal(root);
cout<<endl;
std::cout << "PreOrder Traversal" << std::endl;
PreOrderTraversal(root);
cout<<endl;
std::cout << "PostOrder Traversal" << std::endl;
PostOrderTraversal(root);
return 0;
}
Thank you for reading my content. Be sure to follow and comment on what you want me to write about next 🤓

